In the above code first, we have created a dictionary and assign them key-value pair elements. Now declare a variable and use one single line of code that is the list comprehension method and it is converted into a list of tuples. Tuples are immutable which means, you can't change a tuple once it was created.
Once a tuple was created you can't modify it anymore. Another example of an immutable data type in Python is string. You can't modify tuples or strings in Python, instead, Python creates a new instance with the modified values. However, if a tuple contains mutable data types such as lists, the elements of those lists can change! Yet, the references in the tuple to those lists can't. The Python append() method adds an element at the end of an existing list.
Also, it modifies the existing list instead of creating a new one. The append method can also be used with other Python data types sets and tuples. Lists are sequences that can hold different data types and Python objects, so you can use .append() to add any object to a given list.
In this example, you first add an integer number, then a string, and finally a floating-point number. However, you can also add another list, a dictionary, a tuple, a user-defined object, and so on. In this article, we learned to add variables and values to a tuple in Python by using several methods. We discussed that all these methods cannot change the existing tuple instead created a new tuple.
Adding items to a list is a fairly common task in Python, so the language provides a bunch of methods and operators that can help you out with this operation. With .append(), you can add items to the end of an existing list object. You can also use .append() in a for loop to populate lists programmatically. One thing to keep in mind is that a tuple is immutable. This means that once it's created, you can't modify it in-place.
A list, on the other hand, is mutable — meaning you can add elements, remove elements, and change elements in-place. A list has extra overhead, so only use a list if you need to modify the values. In this example, you just map your key to a list and add tuples to the list.
To perform this particular task we will create a dictionary and assign a key-value element but in this case, the value represents the list. Now declare a variable and use the append function to add a tuple in a dictionary. Here I want to access tuple values in a dictionary.
To do this task first I have to initialize a dictionary with a unique key and a tuple with three values. Now I want to iterate each key to do this we can use the item in the dict() method and this function does not take any argument. It always returns the list will all dictionary elements. In Python, the reverse() method cannot be used in tuples because they are immutable. In the case of the dictionary, we cannot change or reverse the given elements because items in the dictionary are in the form of key-value pairs.
A tuple is a collection of immutable Python objects. It can hold elements of any arbitrary data type (integer, string, float, list, etc.) which makes it a flexible and powerful data structure. It is a part of the Python core language and widely used in Python programs and projects.
In this code example, we are appending a list of tuples as multiple key-value pairs to the dictionary using the dictionary update() method. This method adds items to an already created tuple. It simply converts the original tuple into a list and adds items using append() function of the list. It then converts the new lists back to the tuple. This method is generally used when the user has to pass a tuple as a function argument, which is often necessary for the NumPy functions.
List comprehension along with zip() function is used to convert the tuples to list and create a list of tuples. Python iter() function is used to iterate an element of an object at a time. The 'number' would specify the number of elements to be clubbed into a single tuple to form a list.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use Python to append to a tuple. In this example, we have initialized a list and contains the elements in the form of tuples. Now I want to convert this list into a dictionary to do this I will create a variable and use the dict() method to convert the list into a dictionary.
After that, I will create a new list and use a print statement in which I will pass the 'tuple' keyword as an argument and display the result. Python dictionary update() method takes a sequence as an argument, it can be, a key-value pair, dictionary, tuple, or list of tuples. We will understand how to add multiple key-value pairs in the dictionary.
As we know that Tuples are immutable objects in Python. We cannot perform addition, deletion, modification operations on tuples once created. So, in order to add variables or items in a tuple, we have to create a new tuple instead of modifying the original tuple.
Let us discuss various ways to add variables or values in a tuple. Arrays support most list operations, such as slicing and indexing. Like lists, array.array() also provides a method called .append(). This method works similarly to its list counterpart, adding a single value to the end of the underlying array.
However, the value must have a data type that's compatible with the existing values in the array. The parameter Index Index Index Index Index index must contain a single integer value . Therefore, the first tuple element has got the index 0.
Append Method The append() method in python adds a single item to the existing list. It doesn't return a new list of items but will modify the original list by adding the item to the end of the list. After executing the method append on the list the size of the list increases by one. You can't add elements to a tuple because of their immutable property.
There's no append() or extend() method for tuples, You can't remove elements from a tuple, also because of their immutability. Tuples can contain any number of elements and of any datatype (like strings, integers, list, etc.). Tuples can also be created with a single element, but it is a bit tricky. Having one element in the parentheses is not sufficient, there must be a trailing 'comma' to make it a tuple.
In this example, first we will create a dictionary and assign them key-value pair. Now declare a variable 'new_arr' and pass new_key and new_val variable as a tuple argument. To convert dictionary into array of tuple we can use list comprehension method. Let us see how to add tuples that store multiple values to a single key in a Python dictionary.
In this section, we can see how to iterate over a dictionary in Python. In this example, the keys are a tuple and the values are integer numbers. Now we will use the dict() method and it accepts for loop instance over the list of tuples. In Python the dict() method takes a list of tuples as an argument and each tuple store key-value pair element and it returns into a dictionary. We can make use of the built-in function append() to add elements to the keys in the dictionary.
To add element using append() to the dictionary, we have first to find the key to which we need to append to. Elements of the tuple are immutable and ordered. It allows duplicate values and can have any number of elements.
A tuple's elements can be of any data type (integer, float, strings, tuple, etc.). We cannot change an existing tuple but can create a new tuple and concatenate the old tuple using + operator. If you want to add a single element, make it a singleton like . You can add a tuple of multiple elements with or without that trailing comma.
The trailing comma is necessary for the singleton to avoid confusion between an element in parentheses. This is a special version of the for loop, where there are multiple variables, and the number of variables matches the size of a tuples coming off the list. The above example, looping key,value over dict.items() is probably the most common use of this multiple-variable variant of the for loop. Python provides a method called .append() that you can use to add items to the end of a given list.
This method is widely used either to add a single item to the end of a list or to populate a list using a for loop. Learning how to use .append() will help you process lists in your programs. So far, you've learned how to use .append() to add a single item to a list or to populate lists from scratch. Now it's time for a different and more specific kind of example. Like with several similar methods, .append() changes the underlying list in place. Trying to use the return value of .append() is a common mistake when it comes to learning how mutable sequence types work.
Keeping this behavior of .append() in mind will help you prevent errors in your code. In Python, tuples are immutable i.e. once created we can not change its contents. But sometimes we want to modify the existing tuple, in that case we need to create a new tuple with updated elements only from the existing tuple. Much like strings, tuple values can be altered or appended by simply concatenating a new value onto the existing one. It combines two different sets of tuples into one and doesn't actually change existing values, maintaining the immutability of the data type. Python tuples are one of the main container data structures available within Python.
They are generally created using regular parentheses (). Because they are container data types, they can hold different items and allow items of different data types, meaning that they are heterogeneous. We can also add elements in Tuple, which will return a new tuple type matching the number of elements. For example, if we add value to an element to a Pair then we will get a Triplet object in return.
In this example to iterate over the tuple key we can apply append method and pass 'you_dict' as an argument. Now it will iterate over this list of tuples with the variable name 'new_val'. To access the tuple elements from the dictionary and contains them in a list. We have to initialize a dictionary and pass the tuple key and value as an argument.
Now to get all tuple keys from the dictionary we have to use the Python list comprehension method. In this example, first we will initialize a list with tuples and use the dict() method to convert a list of tuples into a dictionary and print the result. It will display the output in the form of dictionary which contains key-value pair.
This means that elements of a tuple cannot be changed once they have been assigned. But, if the element is itself a mutable data type like a list, its nested items can be changed. When others collaborate with you on your code, your use of tuples will convey to them that you don't intend for those sequences of values to be modified. You can not add, change, remove items in tuples. Tuple represent data that you don't need to update, so you should use list rather than tuple if you need to update it.
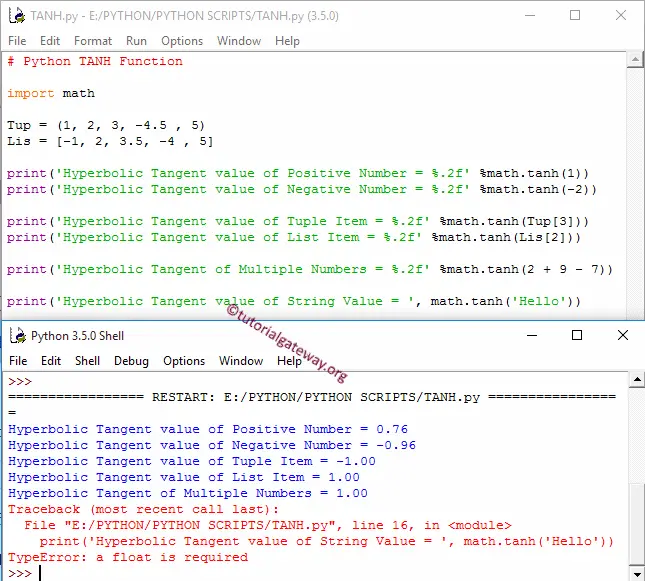
However, if you really need to update tuple , you can convert it to list , update it, and then turn it back into tuple . After writing the above code , Ones you will print " value " then the output will appear as a " ". Here, the tuple will be converted to an array list.


























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.